Black Box Testing: A Complete Beginner-Friendly Guide
Introduction
As a manual tester, I frequently use black-box testing while validating real-time business workflows such as login, payments, and form validations. So let’s understand what black box testing starting from its introduction.
Black-box testing is one of the most widely used software testing techniques in the IT industry. It focuses on validating the functionality of an application without knowing its internal code structure. Testers interact with the software just like end users and verify whether the system behaves as expected.
What is Black Box Testing?
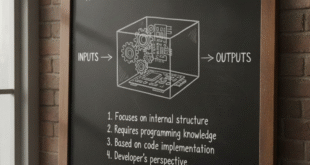
Black-box testing is a software testing method where the tester does not have access to the internal implementation, source code, or logic of the application. The tester provides input and observes output to check if the system works correctly.
In simple words:
➡️ You don’t know how it works inside; you only check what it does.
Why is it called “Black Box”?
The term “black box” represents a system whose internal workings are hidden. The tester can only see:
- Inputs (user actions, data)
- Outputs (system responses, results)
The internal code, design, and architecture remain unknown.
Objectives of Black Box Testing
The main goals are:
- Validate application functionality
- Ensure requirements are correctly implemented
- Detect missing or incorrect features
- Identify interface and integration issues
- Improve overall software quality
Types of Black Box Testing
1. Functional Testing
Verifies whether each function of the application works according to requirements.
Examples:
- Login functionality
- Form submissions
- Payment processing
2. Non-Functional Testing
Focuses on performance and usability rather than functionality.
Examples:
- Performance testing
- Load testing
- Usability testing
3. Regression Testing
Ensures new changes do not break existing functionality.
4. Acceptance Testing
Performed to confirm the application is ready for release.
Examples:
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
- Business Acceptance Testing (BAT)
Black Box Testing Techniques
1. Equivalence Partitioning
Input data is divided into valid and invalid groups. One value from each group is tested.
Example:
Age field allows 18–60
- Valid: 25
- Invalid: 15, 65
2. Boundary Value Analysis
Focuses on testing boundary values where defects are most common.
Example:
Range: 1–100
Test values: 0, 1, 100, 101
3. Decision Table Testing
Used when multiple conditions and rules exist.
Example:
Login based on:
- Valid username
- Valid password
4. State Transition Testing
Checks system behavior when transitioning between different states.
Example:
Account status:
- Active → Locked → Unlocked
5. Error Guessing
Based on the tester’s experience and intuition.
Example:
- Leaving mandatory fields blank
- Entering special characters in input fields
Advantages of Black Box Testing
✅ No programming knowledge required
✅ Tester perspective matches end-user behavior
✅ Effective for large systems
✅ Helps identify requirement gaps
Limitations of Black Box Testing
❌ Limited coverage of internal logic
❌ Test cases depend heavily on the requirement quality
❌ Some defects may remain hidden
Black-Box vs White-Box Testing
| Aspect | Black-Box | White-Box |
|---|---|---|
| Code Knowledge | Not required | Required |
| Focus | Functionality | Internal logic |
| Performed by | Testers, QA | Developers |
| Level | System & Acceptance | Unit & Integration |
Real-Life Example
Testing an ATM machine:
- Insert card
- Enter PIN
- Withdraw cash
- Check balance
You don’t know how the ATM software processes transactions internally—you only verify expected results. That’s black-box testing.
Conclusion
Black-box testing plays a vital role in ensuring software meets user expectations and business requirements. It is easy to learn, efficient, and essential for every tester—especially manual testers starting their QA journey.
Mastering black-box testing techniques enables testers to design effective test cases, identify critical defects, and deliver high-quality software.
Learn more topics about Manual Testing